Routes in Issabel PBX
In
Issabel PBX, routes are essential configurations that define how calls are directed within and outside the PBX system. Routes ensure that calls reach their intended destinations, whether they originate from internal extensions, external phone lines, or inbound calls from the PSTN or VoIP providers. Definition of Routes
Routes are configurations that define how calls are directed within the system. They specify the path a call should take to reach its destination, whether the call originates from inside the PBX (an internal extension) or from outside (external lines or trunks). Routes ensure that calls are processed correctly based on predefined rules. Routes are essential for: - Managing incoming calls from external numbers.
- Directing outgoing calls from internal users to the outside world.
- Organizing and prioritizing communication flows within the
PBX.
Types of Routes
1. Inbound
Routes:- Handle incoming calls from external sources.
- Direct calls to internal destinations such as extensions, IVRs, queues, or voicemail.
- Commonly associated with DIDs (Direct Inward Dialing) and/or caller ID patterns.
2. Outbound
Routes:- Manage outgoing calls from internal extensions to external numbers.
- Define how calls are sent to trunk lines (e.g., PSTN, SIP trunks).
- Often configured with dial patterns to ensure proper routing based on the number dialed.
Routes configuration
Configuring inbound and outbound
routes in Issabel PBX is essential to manage the flow of calls, both incoming and outgoing. These routes determine how calls are handled based on their origin and destination, allowing efficient control of telephone traffic. Based on routes configurations, it is possible to establish a system that optimizes communication for both agents and customers, improving overall operational efficiency. Inbound Routes
These
To create and configure and Inbound
routes manage how calls coming from the outside world are handled by the PBX. They are critical for routing incoming calls to the correct internal destinations, such as IVRs, extensions, queues, or ring groups. To create and configure and Inbound
route, it is necessary to login into the PBX´s web interface with an account that has administrative permissions. Then, navigate to PBX → PBX Configuration → Connectivity → Inbound Routes. 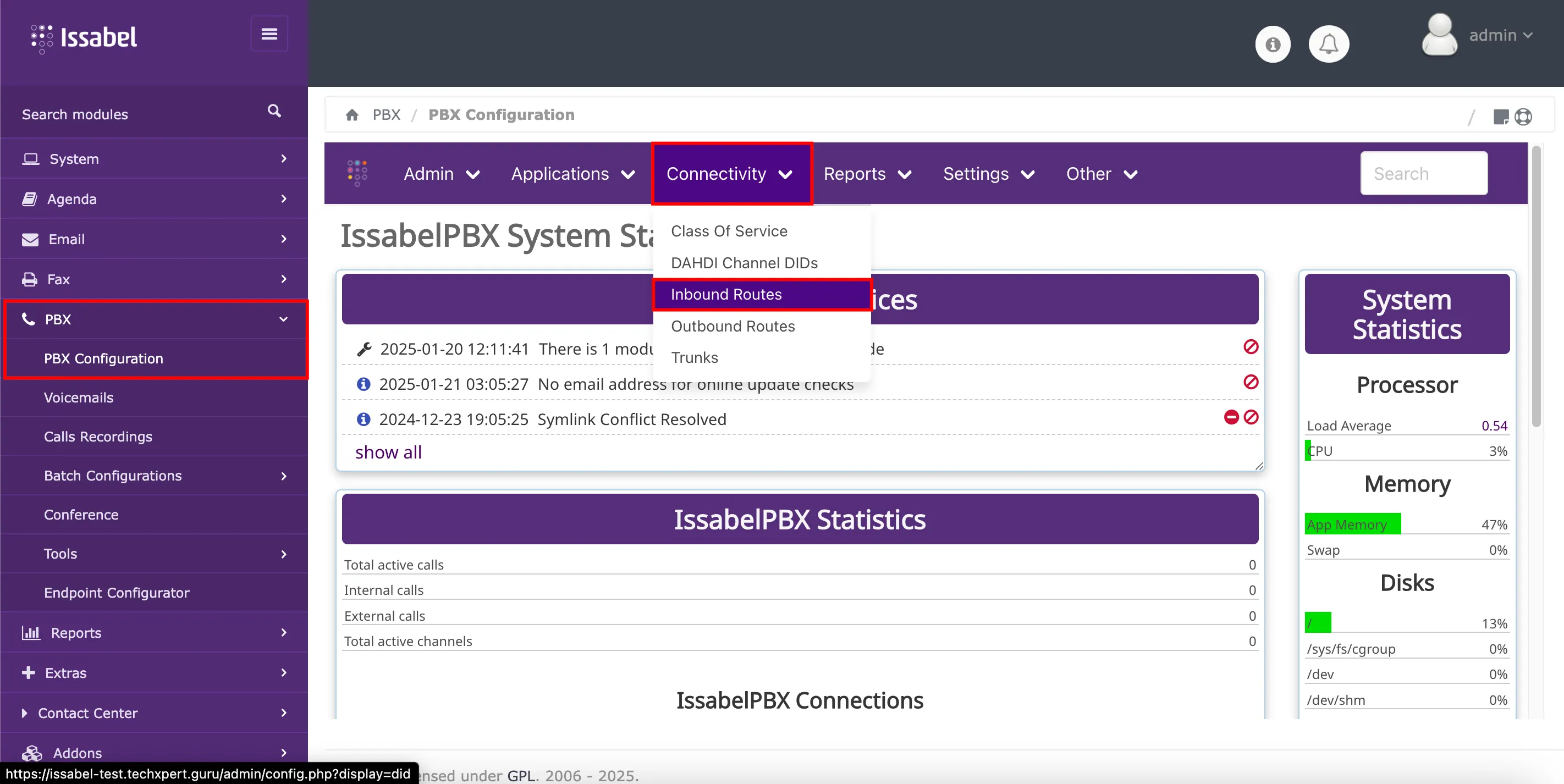
Inbound Routes Parameters
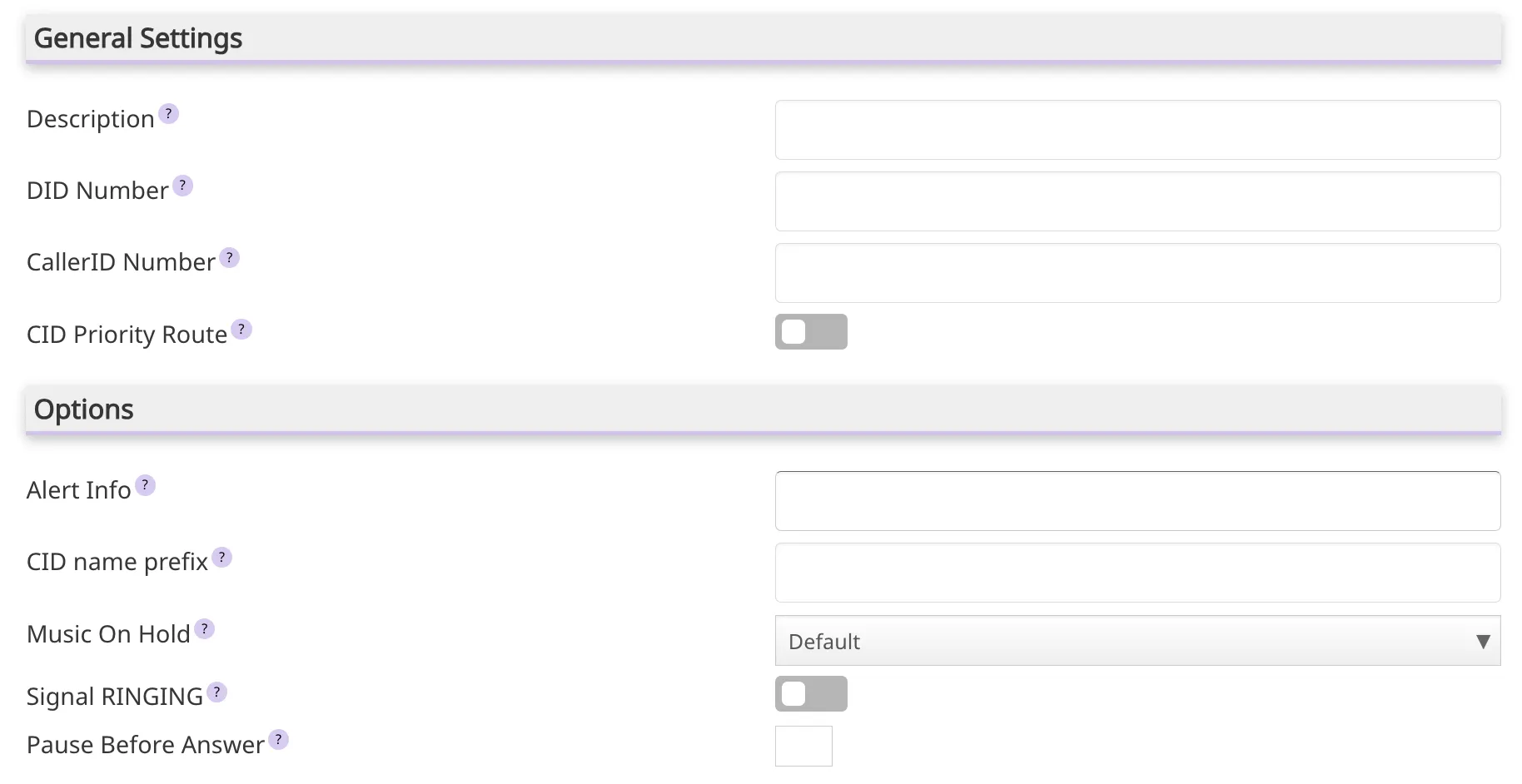
A for will be displayed to create a new inboud
route. The main parameters of these type of routes are described bellow: - Description: Field to provide a description to identify the
route. - DID (Direct Inward Dialing) Number: Field to enter the number that will be used to
routecalls. This can be a specific number or a pattern. - Caller ID Number: Allows routing based on the incoming caller’s phone number.
- Caller ID Priority Route: This effects CID ONLY routes where no DID is specified. If checked, calls with this CID will be routed to the
route, even if there is arouteto the DID that was called. Normal behavior is for the DIDrouteto take the calls. If there is a specific DID/CIDroutefor the current Caller ID, thatroutewill still take the call when that DID is called.
Outbound Routes
These
To create and configure and Outbound
routes manage calls initiated from the PBX (internal extensions) to external numbers. They define how these calls are processed and which trunk is used. To create and configure and Outbound
route, it is necessary to login into the PBX´s web interface with an account that has administrative permissions. Then, navigate to PBX → PBX Configuration → Connectivity → Outbound Routes. 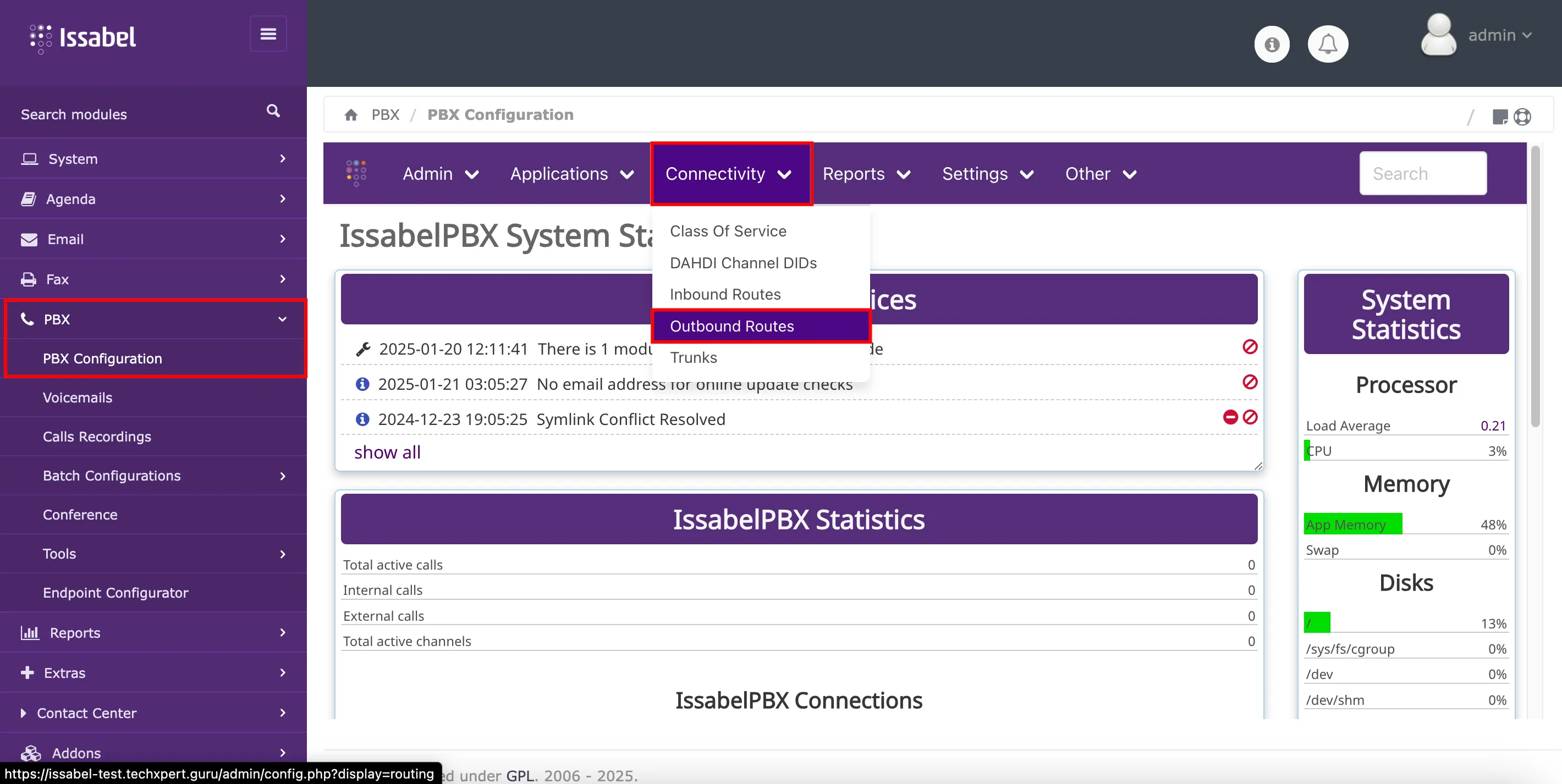
Outbound Routes Parameters
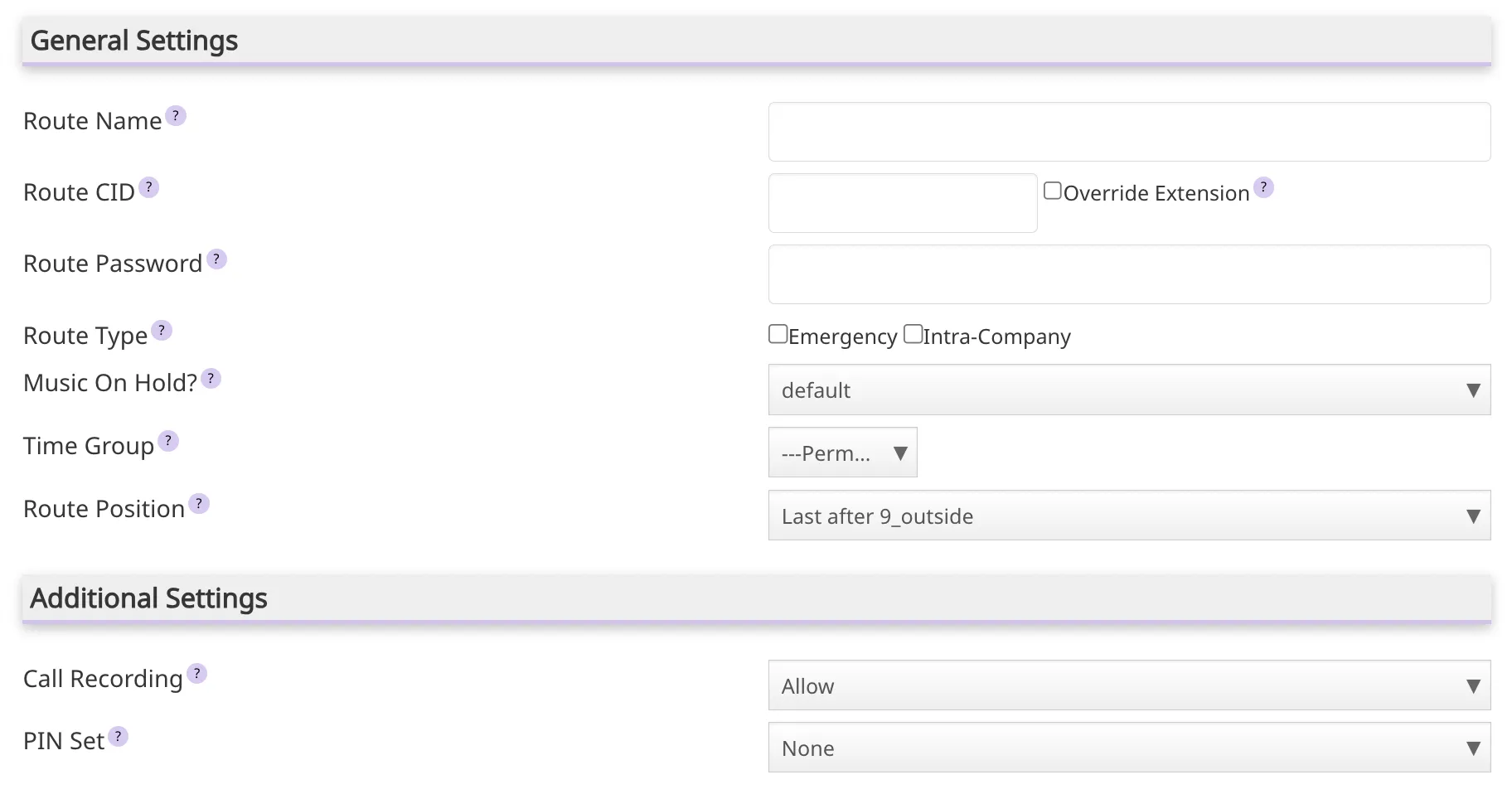
A for will be displayed to create a new outbound
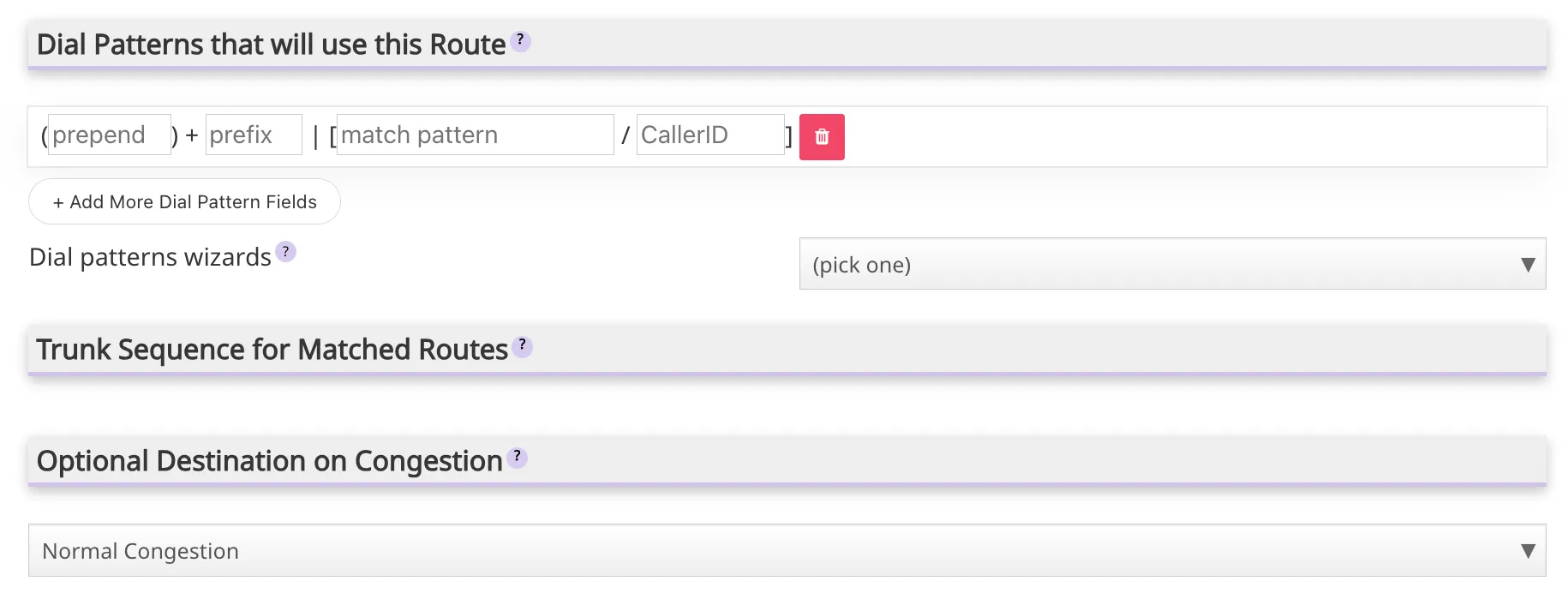
route. The main parameters of these type of routes are described bellow: RouteName: Field to assign a descriptive name that facilitates identification.- Dial Patterns:
- Define the format of numbers that should use this route.
- Patterns typically include: Specific prefixes, area codes or country codes, wildcards to match multiple numbers, among others.
- Example Dial Patterns:
- 9|NXXXXXX → Strips the 9 and routes 7-digit local numbers.
- 1NXXNXXXXXX → Matches 11-digit long-distance numbers in the U.S.
- 011. → Matches international calls starting with 011.
- Trunk Sequence for Matched
Routes:- Outbound
routesdefine which trunk (PSTN or VoIP provider) will handle the call. - Trunks are selected in order of priority. If the first trunk fails, the system tries the next one.
- Outbound
RouteCaller ID: Optional Route CID to be used for theroute. If set, this will override all CIDS specified except:- Extension/device EMERGENCY Caller IDs if the current route is checked as an EMERGENCY Route.
- Trunk Caller ID if trunk is set to force it's Caller ID.
- Forwarded call Caller IDs (CF, Follow Me, Ring Groups, etc).
- Extension/User Caller IDs if checked.
RoutePassword:- A
routecan prompt users for a password before allowing calls to progress. This is useful for restricting calls to international destinations or 1-900 numbers. - A numerical password, or the path to an Authenticate password file can be used.
- Leave this field blank to not prompt for password.
- A
RouteType:- Selecting Emergency will enforce the use of a device's Emergency Caller ID setting (if set). Select this option if this
routeis used for emergency dialing (ie: 911). - Selecting Intra-Company will treat the
routeas an intra-company connection, preserving the internal CallerID information instead of the outbound CID of either the extension or trunk.
- Selecting Emergency will enforce the use of a device's Emergency Caller ID setting (if set). Select this option if this
RoutePosition: Where to insert therouteor relocate it relative to the otherroutes.- Pin Set: Select a PIN set to use. If using this option, leave the
RoutePassword field blank.
Best Practices for configuring Routes
1. Use Specific Patterns: Avoid overly generic patterns to prevent calls from being misrouted.
2. Set Priorities: Avoid overly generic patterns to prevent calls from being misrouted.
3. Secure Outbound Routes: Restrict access to high-cost routes (e.g., international) to prevent misuse or fraud.
4. Test Routinely: Periodically test inbound and outbound routes to ensure proper functionality.
5. Document Configurations: Maintain records of route settings for troubleshooting and updates.
Common use cases for Routes
Inbound Routes:
- Multi-Department Call Routing: Use DIDs to route calls to specific departments automatically.
- VIP Routing: Route calls from specific customers to priority agents.
- Time-Based Routing: Direct calls to live agents during business hours and voicemail after hours.
Outbound Routes:
- Cost Optimization: Route calls to the cheapest available trunk based on call type (local, national, international).
- Backup Routing: Use secondary trunks for failover in case of primary trunk failure.
- Restriction Policies: Restrict access to specific trunks for certain users or extensions.
Advantages of proper Route configuration
1. Efficient Call Handling: Ensures calls are directed quickly and accurately to the right destination.
2. Cost Savings: Routes calls via the most cost-effective trunk or provider.
3. Reliability: Failover options provide backup during outages.
4. Enhanced Security: Prevents unauthorized use of high-cost outbound routes.
5. Improved Customer Experience: Customized inbound routes ensure callers reach the desired department efficiently.
Routes in Issabel PBX are fundamental for managing both inbound and outbound calls. By configuring routes effectively, businesses can optimize call handling, reduce costs, and enhance the overall telephony experience for both customers and employees. Proper use of dial patterns, trunk prioritization, and time-based routing ensures a flexible and reliable communication system. Like all pbx configuration modules, in the inboud and outbound
routes module, each configurable field has a question mark on the right side of its name, and when you hover the mouse or click on this sign, important information about the field is displayed, the which can serve as a guide for its configuration. If there is any incorrect or incomplete information, or additional information needs to be generated, please write to isscc@issabel.com