Trunks in Issabel PBX: A Comprehensive Overview
In
To access the
Once there, within the top navigation bar menu, it is necessary to open the drop-down menu for: Connectivity, and select the option:
Issabel PBX, a trunk is a communication pathway that connects the PBX system to an external network, such as the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), VoIP providers, or another PBX system. Trunks are essential for enabling inbound and outbound calls and serve as the backbone of call routing and connectivity in the PBX environment. To access the
trunk module, is necessary to enter the PBX administration interface with an account that has administrative permissions. Within the list in the sidebar, it is necessary to open the drop-down menu for: PBX, and select the option: PBX Configuration. Once there, within the top navigation bar menu, it is necessary to open the drop-down menu for: Connectivity, and select the option:
Trunks. 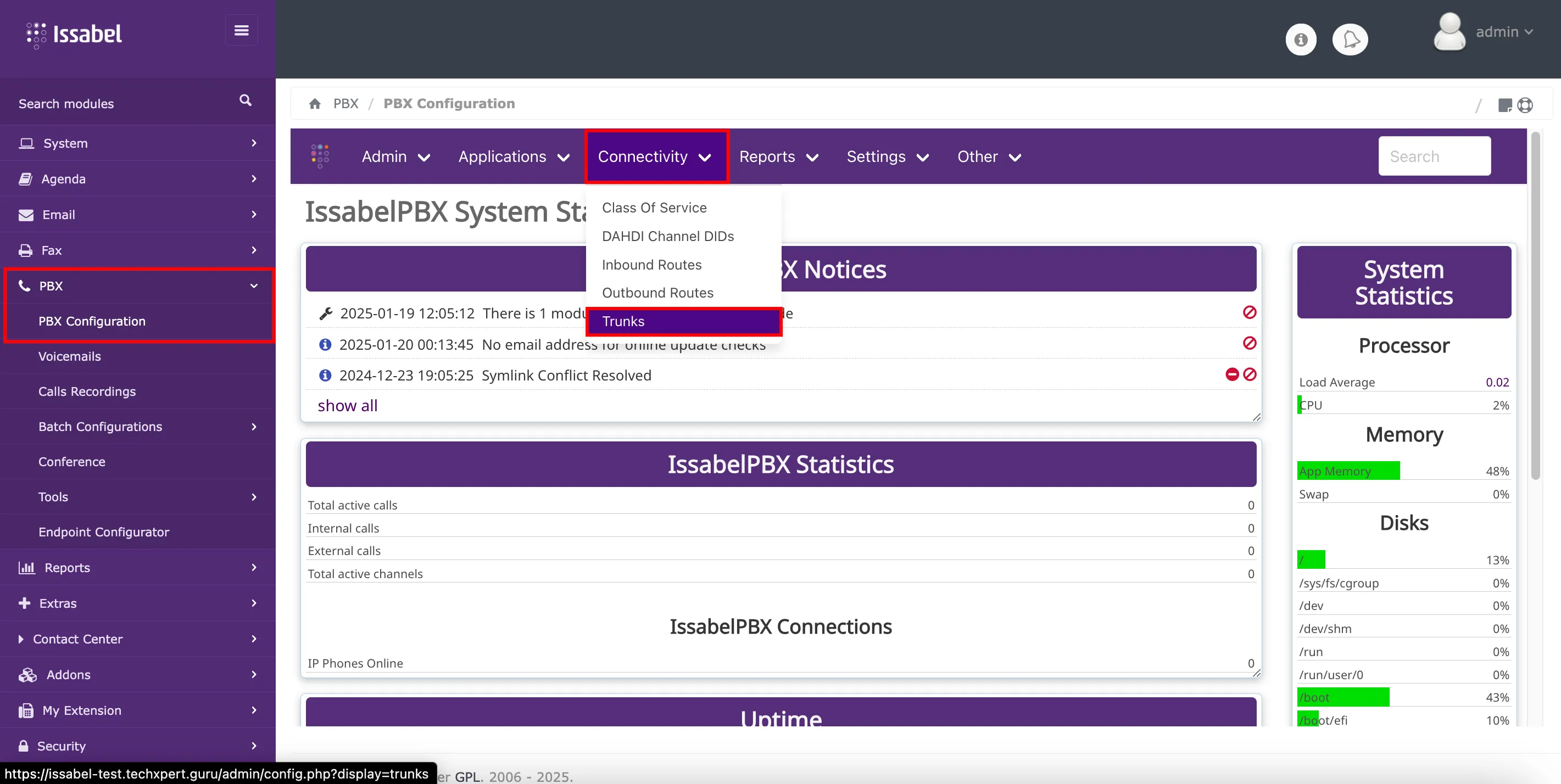
Definition of Trunks
A
trunk is essentially a configuration that defines how Issabel PBX communicates with external systems or service providers. It acts as a bridge for sending and receiving voice traffic. Trunks can be physical (e.g., ISDN lines) or virtual (e.g., SIP or IAX trunks). Types of Trunks in Issabel PBX
Issabel PBX supports several types of trunks, depending on the communication method: 1. SIP
Trunks:- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
trunksare the most common type used in modern VoIP systems. - They use the internet to transmit voice traffic and are highly scalable and cost-effective.
- SIP
trunksare configured with details like the provider's SIP server address, username, password, and registration details.
2. IAX
Trunks:- IAX (Inter-Asterisk eXchange)
trunksare an alternative to SIP, often used for Asterisk-based systems. - IAX is particularly efficient for traversing NAT and can multiplex multiple calls into a single UDP stream.
- Ideal for connecting two Asterisk-based PBX systems.
3. DAHDI/Analog
Trunks:- These
trunksuse physical analog lines or Digital Access Hybrid Device Interface (DAHDI) for connectivity. - Commonly used with traditional PSTN or ISDN lines.
- Requires compatible hardware cards installed on the PBX server.
4. Custom
Trunks:- Custom configurations for advanced or non-standard setups.
- Allows integration with specialized systems or protocols.
Trunk Configuration
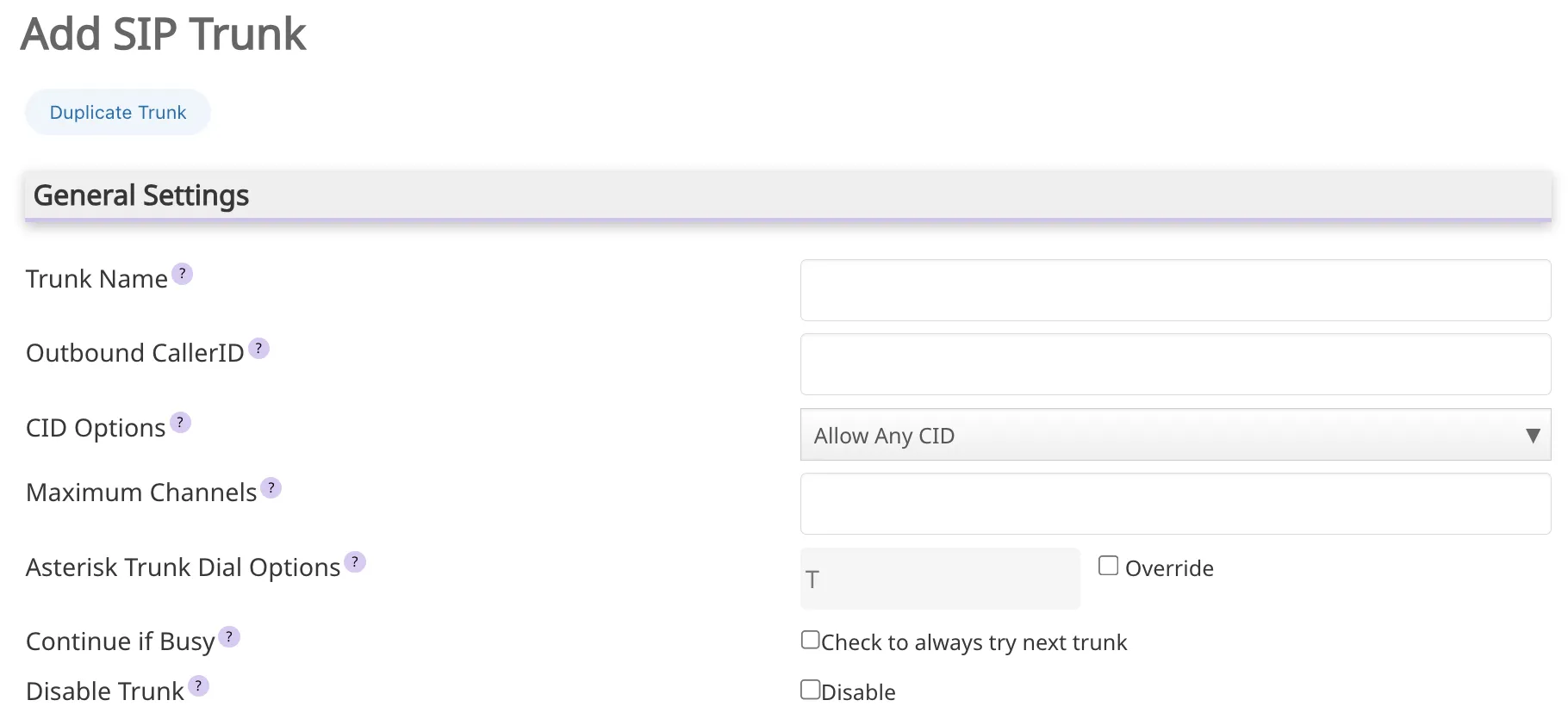
Configuring SIP
trunks in Issabel Contact Center is essential to allow communication between the Contact Center system and the public telephone network (PSTN). By configuring trunks based on best practices, you can ensure smooth, high-quality communication for both internal and external calls. Below are the most important parameters to consider to create and configure SIP trunks effectively, which are the most widely used. A form for creating a
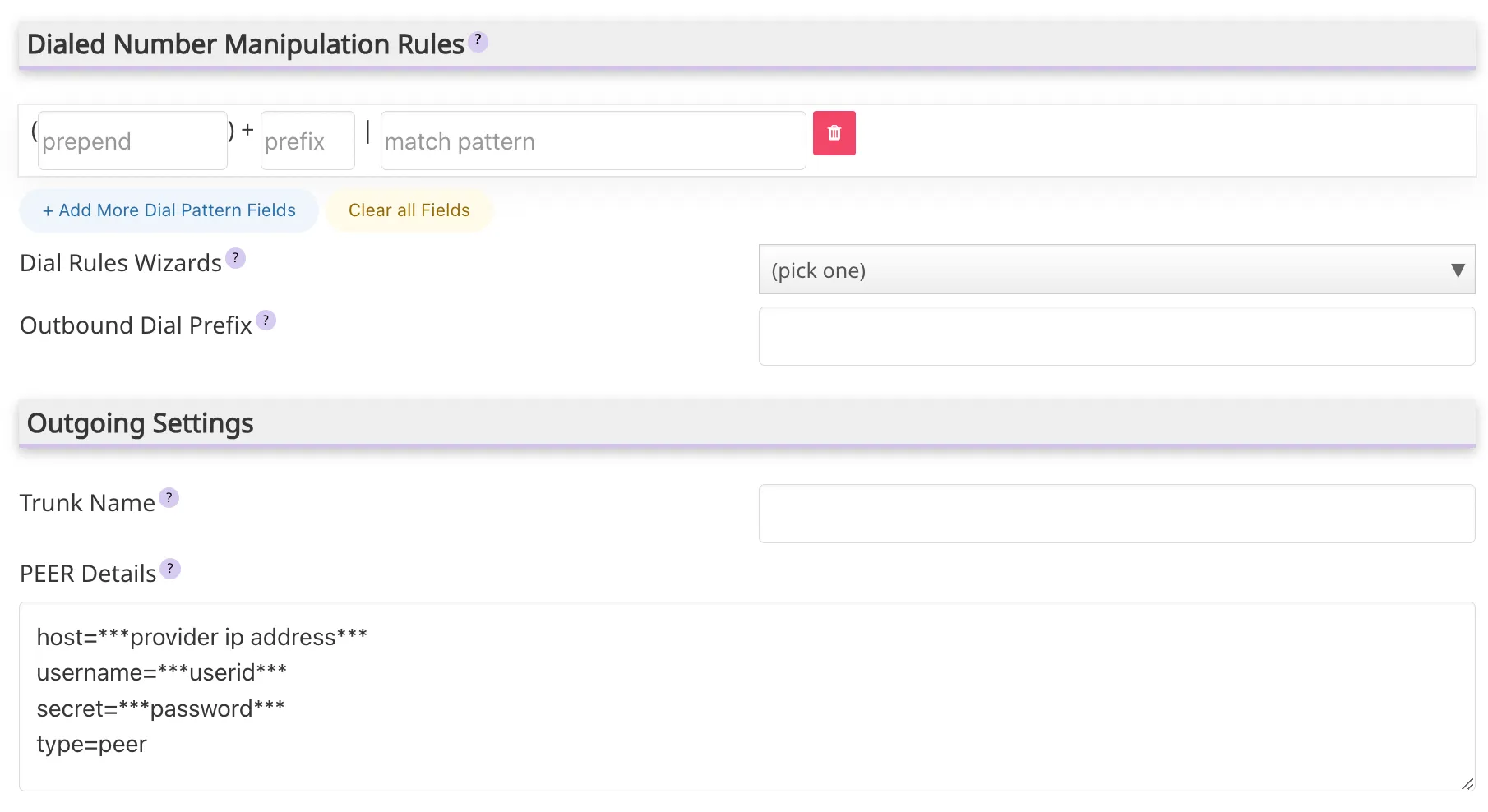
queue will appear. Below are the most important parameters to create and configure queues in Issabel PBX. TrunkName: Field for the assignation of a friendly name for easy identification (for example, "SIP Trunk Provider X").- Peer details: These are the connection parameters with the service provider. These may vary according to the type of
trunkline and the specifications received by the provider. - Port: Is the connection port, generally it is 5060, unless your provider indicates otherwise.
- User: Field to provide the username (extension ID) provided to you by the provider.
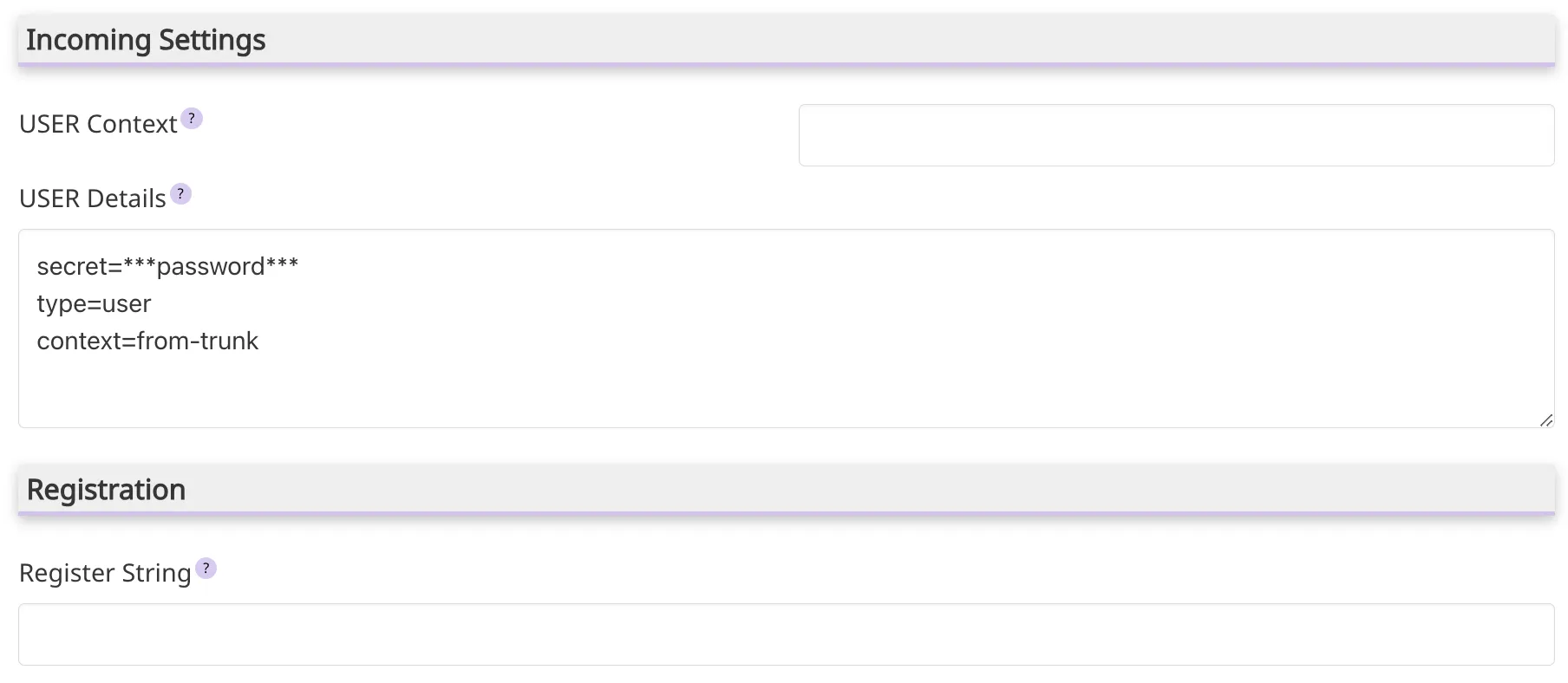
- User Details: Field to provide user details (username, password, among others) for the connection with the service provider. The format may vary depending on the type of
trunkline and the provider.
Types of Trunks in Issabel PBX
Trunks are used to enable communication for various scenarios: 1. Inbound Calls:
Trunksreceive calls from external networks and route them to the PBX system.- Example: A customer dials a company's public phone number (via a PSTN line or SIP DID), and the call is routed to an internal extension or queue.
2. Outbound Calls:
Trunksenable internal PBX users to make external calls.- Example: An employee dials an external number, and the call is routed through the SIP trunk to the destination.
3. PBX-to-PBX Connectivity:
Trunksconnect multiplePBXsystems for seamless communication between offices or branches.- Example: A SIP
trunkconnects the main office PBX with a branch office PBX.
Advantages of Trunks in Issabel PBX
1. Cost-Effectiveness:
- SIP
trunksreduce costs compared to traditional PSTN lines, especially for long-distance or international calls.
2. Scalability:
- Virtual
trunkslike SIP or IAX can easily scale to accommodate increased call volumes.
3. Flexibility:
- Supports multiple types of
trunks, allowing integration with various providers and systems.
4. Reliability:
- Failover options ensure uninterrupted communication by automatically switching to backup
trunksif the primary one fails.
5. Advanced Features:
Trunksenable features like DID (Direct Inward Dialing), which allows routing calls to specific extensions based on the number dialed.
Trunk Configuration in Issabel PBX
To configure a
trunk in Issabel PBX:1. Access the PBX Configuration:
- Log in to the
Issabel PBXAdministration interface. - Navigate to
PBX→PBX Configuration→Connectivity→Trunks. - Select the required type of
trunk(SIP,PJSIP,DADHi,IAX2,ENUM,DUNDi,Custom).
2. Set
Trunk Details:- Fill in the required fields, including
trunkname, outgoing settings, and registration details.
3. Test the
Trunk:- Make test calls to ensure the
trunkis configured correctly for both inbound and outbound communication.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
1. Registration Issues:
- Check the registration string format and credentials.
- Verify the connectivity to the provider's server.
2. Call Quality Issues:
- Adjust codec preferences to match the provider's requirements.
- Ensure sufficient bandwidth for VoIP calls.
3. Outbound Call Failures:
- Verify dial patterns in the outbound routes.
- Check if the trunk is correctly selected for outbound calls.
4. Inbound Call Failures:
- Ensure DID routing is correctly configured.
- Verify the incoming settings of the
trunk.
Trunks are a fundamental part of Issabel PBX, enabling seamless communication with external networks and systems. By understanding the different types of trunks and their configurations, administrators can optimize call routing, improve reliability, and reduce costs. Properly configured trunks ensure a robust and scalable telephony solution for businesses of all sizes. Like all pbx configuration modules, in the
trunks module, each configurable field has a question mark on the right side of its name, and when you hover the mouse or click on this sign, important information about the field is displayed, the which can serve as a guide for its configuration. If there is any incorrect or incomplete information, or additional information needs to be generated, please write to isscc@issabel.com